Technical Information
Detail info about Technical Information
Nem Alma Cihazı Uygulamaları
Why Dehumidify Intrduction
In the following sections we will explain the basics of sorption dehumidifying. Why you need it, how it works and how you estimate your need for dehumidifying.

CORROSION
Iron and steel will not rust if the air in contact with the surface has a humidity below 50% relative humidity (RH). Dehumidification is often a better and less expensive way to protect investments than painting. Objects that are protected by dehumidification are for example bridges, power stations , boats (during refitl) and offshore constructions.
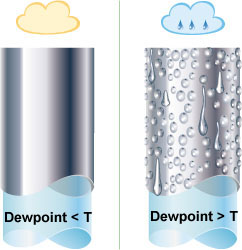
CONDENSATION
Moisture will not condensate on a surface if the air in contact with it has a dew-point lower than the surface temperature. Condensation can lead to many problems such as corrosion or short-circuit in electrical systems.

ICE FORMATION
Ice will not form on a surface if the air in contact with it has a dew-point lower than the surface temperature. Ice formation is a problem in for example cold storages where it will cause a lower efficiency in the cooling machinery. Dehumidification will keep the ice away.
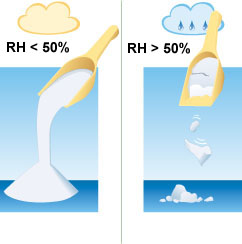
HANDLING OF HYGROSCOPIC MATERIALS
The quality of dry drugs, dry food, hard candy and other hygroscopic materials can only be maintained through production to the consumer if it is kept in contact with air at a low relative humidity. If your products form lumps, degrade quickly, or get sticky you should consider dehumidification. Most materials demand dew-points so low that they can only be achieved by sorption dehumidifiers.

DRYING BUILDINGS
When removing moisture from a building, whether it is a new building or a building with water damage, the most effective way is to use sorption dehumidifying. Heating will only move the moisture to another part of the building, heating in combination with outdoor ventilation will create high energy costs. With sorption dehumidifying the moisture is removed from the building in a very energy efficient way.

MOULD
Mould and fungus formation is prevented if the surrounding air is kept below 70%RH. This is important in many situations, for example in storage of wooden products. In houses designed with a crawl space it is often necessary to use a dehumidifier to keep mould and fungus from forming.

ODOURS
Unpleasant odours, will be significantly reduced if the relative humidity is kept below 50%RH. For example , in sewage stations the odours can be controlled by installing a dehumidifier.
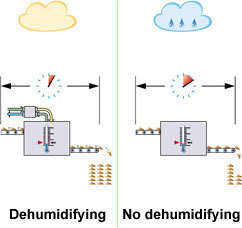
PRODUCT DRYING AND COOLING
When drying and cooling products a low relative humidity is essential for a fast process. If the products to be dried are sensitive to high temperature, the low relative humidity can only be obtained with dehumidification. In cooling processes dehumidification allows for a lower temperature without condensation. The result is faster cooling and money saved.

ELECTRONICS
The characteristics of electronic products are changed at high relative humidity.
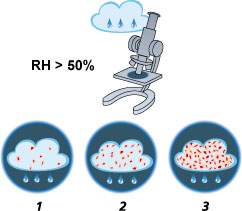
BACTERIA
Bacteria need humidity to survive and multiply. Often the humidity required for bacteria to multiply is found on hygroscopic materials. If the surrounding air is held below 50% relative humidity most bacteria will not find a suitable environment to multiply.
Gas Phase Filtration (Chemical Filter) Applications
Air borne contaminations are in solid, liquid and gas phases. In ventilation sector, for contamination filtration generally particle filters are used and these particle filters can filter only solid particles. Liquid phase contaminations are filtered by mist eliminators or condensing equipments, while gas contaminations are filtered by chemical filters.
Gas phase filtration or chemical filters are used in industrial and water treatment facilities for odor control and equipment-process reliability, in commercial buildings to increase indoor air quality (IAQ 62.1) and energy saving.
Moisture Load Calculation
For moisture load calculation you can use online calculator.
DST Online Moisture Load Calculation Program
Important Points For Duct Leakage Test
- The test pressure must not exceed 1000 Pa for A and B class manufactured ducts or maximum design pressure if less than 1000Pa. For C Class ductworks inlet static pressure can be increased up to 2000 Pa. At test procedure the working pressure can be given preference as test inlet duct pressure.
- Min. 10 m² duct surface area can be tested with this test device. Test area must be min. 10% for circular duct systems and must be 20% for rectangular duct systems.
- The hygienic duct systems must be completely tested.
- If you can not reach the enough test pressure with 50 hz frequency of frequency inverter, it’s meaning you have more leakages. If you reduce the amount of leakages you can easily reach the test pressure.
- Generally the flanges, elbows, gaskets, fittings and collectors have the more leakages. For preventing the leakages you have to check the gaskets and apply silicon to the connection points.
- Visual detection of leakages are made by smoke generator. If smoke generator model is used than smoke generator user guide has to be read and obeyed to the operating manual. Device is getting extremely hot while working, so it has not been touched with bare hands during working and after use. In the case of respiration the smoke, it can cause respiratory diseases. Smoke liquid consist alcohol and can flare and burn.
- Electrical connections have to be grounded to prevent electrical shocks.
- Tests must be completed before insulation.
Air Filter Technology
- Oil Thread Leak Test (EN 1822-4)
- EMERY (DOP) Test (ISPE)
- Scan Test Method (EN 1822-4)